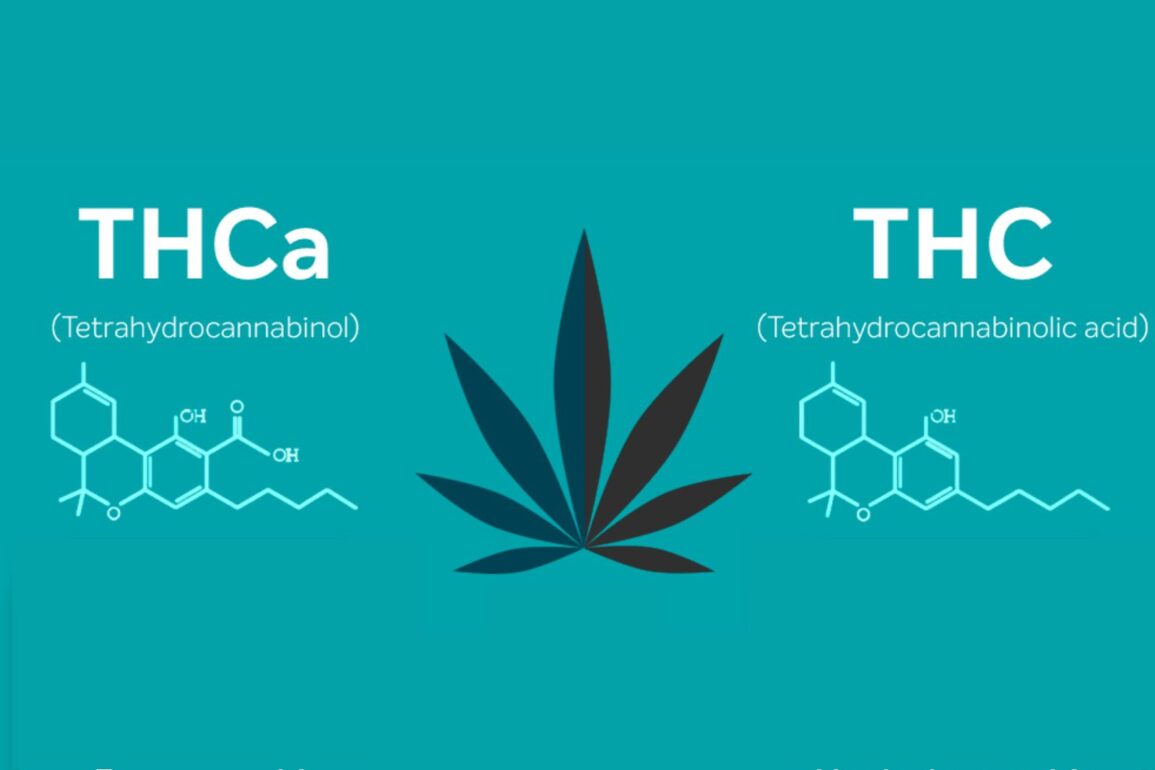
THCA and THC are two compounds found in the cannabis plant, and they play crucial roles in its effects and potential therapeutic benefits. Know THCA and THC: What’s the Difference.
Table of Contents
- What is THCA vs. THC
- Understanding The Difference Between THC and THCA
- What is THC?
- THCA legality?
- What is THCA?
- How to Get THCA?
- Is THCA Psychoactive?
- How does THCA interact with the human body?
- Potential benefits and effects of THCA
- How THCA becomes THC?
- FAQs
- The Bottom Line
What is THCA vs. THC
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the compounds found in the cannabis plant, primarily THC and THCA.
Understanding The Difference Between THC and THCA
These two compounds have gained significant attention due to their potential health benefits and psychoactive effects. However, they are distinct entities with different properties. Let’s examine the difference between THC and THCA, their legal status, and how to obtain them.
What is THC?
THC, short for tetrahydrocannabinol, is the most well-known and abundant psychoactive compound found in cannabis. It is responsible for the “high” or euphoric feeling experienced by recreational users. THC works by binding to the cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system, altering neurotransmitter release and leading to its psychoactive effects.
THC has both medicinal and recreational applications. Medical research has shown that THC can help alleviate symptoms associated with chronic pain, nausea, and muscle spasms. However, its recreational use has been controversial due to its psychoactive nature and potential for abuse.
THCA legality?
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the non-psychoactive precursor of THC. When the cannabis plant is raw, it contains THCA rather than THC. THCA only converts to THC when exposed to heat or sunlight through decarboxylation. As a result, raw cannabis, such as fresh leaves or buds, does not produce the euphoric effects commonly associated with THC consumption.
THCA is not considered an illegal substance in many jurisdictions because it lacks psychoactive properties. However, the legal status of THCA can vary depending on regional regulations, so it’s essential to research local laws before using or possessing products containing THCA.
What is THCA?
As mentioned earlier, THCA is the acidic form of THC. It is abundant in raw cannabis plants and offers potential health benefits without causing intoxication. Some studies suggest that THCA may have anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anticancer properties. However, further research is needed to fully understand its potential therapeutic effects.
Consuming THCA in its raw form, such as by juicing fresh cannabis leaves, allows individuals to benefit from its potential health properties without experiencing the high typically associated with THC consumption. This alternative consumption method is gaining popularity among health-conscious cannabis users.
Keeping It Simple
In summary, THC is the psychoactive compound responsible for the “high” in cannabis, while THCA is the non-psychoactive precursor that converts to THC through decarboxylation. THCA is legal in many places, but its legal status may differ based on regional regulations.
THC vs. THCA
The main difference between THC and THCA is their psychoactivity. THC induces the well-known euphoric effects, making it popular for recreational use but also valuable for medicinal applications. THCA, on the other hand, is non-psychoactive and has shown promise as a potential therapeutic compound.
Keeping Things Legal
Regarding legality, it’s crucial to stay informed about the regulations governing cannabis products in your area. In many places, products containing THC are subject to strict restrictions, while THCA-based products may offer a more accessible and legal alternative.
How to Get THCA?
As mentioned earlier, THCA is found in raw cannabis plants.
To obtain THCA without experiencing the psychoactive effects of THC, one can consume fresh cannabis leaves, buds, or tinctures made from raw cannabis. Applying heat, such as smoking or vaporizing, will convert THCA to THC, potentially producing psychoactive effects.
Is THCA Psychoactive?
THCA is non-psychoactive but can become psychoactive when decarboxylated into THC. It’s essential to avoid exposing THCA-rich products to high temperatures if you wish to avoid the psychoactive effects.
Getting the Most THCA in Your Products
If you want to maximize THCA content in cannabis products, consider opting for products made from raw or minimally processed cannabis. Some manufacturers may also label their products with THCA percentages, allowing consumers to make informed choices.
How does THCA interact with the human body?
THCa, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a non-psychoactive compound in raw cannabis. Unlike THC, it does not directly interact with the endocannabinoid receptors in the brain. Instead, THCa primarily interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) indirectly, influencing its functions.
The ECS is a complex system of neurotransmitters, receptors, and enzymes that regulate various physiological processes, such as mood, appetite, pain, and inflammation. THCa may interact with the ECS by inhibiting the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), responsible for breaking down anandamide, an endocannabinoid associated with feelings of happiness and well-being. By inhibiting FAAH, THCa may indirectly increase anandamide levels in the body, potentially promoting relaxation and well-being.
Potential benefits and effects of THCA
While research on THCa is still in its early stages, some studies suggest possible uses and impacts associated with this compound. These may include
- Anti-inflammatory properties: THCa has shown promise as an anti-inflammatory agent, potentially relieving individuals with inflammatory conditions like arthritis.
- Neuroprotective effects: Some research indicates that THCa may have neuroprotective properties, which could benefit neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s.
- Anti-emetic properties: THCa has been studied for its potential to alleviate nausea and vomiting, making it potentially useful for patients undergoing chemotherapy.
- Antioxidant properties: THCa acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative stress and potential damage caused by free radicals.
- Enhanced mood and well-being: As mentioned earlier, THCa’s indirect influence on the ECS may contribute to improved mood and a sense of relaxation.
How THCA becomes THC?
THCa is the acidic precursor of THC found in raw cannabis. When the cannabis plant material is exposed to heat or sunlight, decarboxylation occurs, converting THCa into THC. This conversion involves the removal of a carboxyl group (COOH) from THCa, resulting in the formation of THC. This decarboxylation process typically happens during smoking, vaporization, or cooking with cannabis-infused products.
THCa vs. THC
The primary difference between THCa and THC lies in their psychoactivity. THCa is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce the intoxicating “high” associated with THC consumption. On the other hand, THC is psychoactive and interacts directly with the brain’s cannabinoid receptors, leading to the euphoric effects commonly experienced with cannabis use.
THCa vs. THCV
THCV, or tetrahydrocannabivarin, is another cannabinoid found in cannabis. Unlike THCa, THCV is psychoactive but possesses different effects compared to THC. THCV may act as an appetite suppressant, potentially helping with weight management. It also appears to have other products on the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, contributing to its unique pharmacological profile.
THCa vs. THC drug test
Standard drug tests typically look for THC metabolites in urine, blood, or hair samples. Since THCa is non-psychoactive and does not convert to THC until it undergoes decarboxylation, consuming THCa-rich products should not trigger a positive drug test for THC. However, individuals should be cautious with products that may contain traces of THC due to incomplete decarboxylation or contamination during processing.
FAQs
Is THCA legal?
THCa itself is typically legal in most places since it is non-psychoactive. However, the legal status of cannabis and cannabis-derived products, including those containing THCa, can vary depending on regional regulations. Always check local laws to ensure compliance.
Why does THC get you elevated and THCA doesn’t?
THC is psychoactive because it directly binds to the CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the brain, leading to alterations in neurotransmitter release and euphoric effects. In contrast, THCa does not bind to CB1 receptors, and its non-psychoactive nature is due to the absence of the carboxyl group that triggers the typical THC response.
Is THCA intoxicating?
No, THCa is non-intoxicating. As a non-psychoactive compound, THCa does not induce the intoxicating effects commonly associated with THC.
Will THCA make me fail a drug test?
Consuming THCa-rich products should not cause a positive drug test for THC, as THCa itself is not the compound targeted in standard drug tests. However, exercise caution with products containing potential THC traces, especially if you are subject to regular drug testing.
The Bottom Line
Understanding the difference between THC and THCA is crucial for cannabis users seeking specific effects from their products. THC provides psychoactive effects and has both medicinal and recreational applications, while THCA is non-psychoactive and offers potential health benefits. By staying informed about the legal status and consumption methods, users can make responsible choices that align with their preferences and health goals. As research on cannabis compounds continues to expand, we can expect more insights into the potential benefits and applications of both THC and THCA. Always consult with a healthcare professional before using cannabis products for medicinal purposes.
Disclaimer – The contents of this article are provided solely for informational purposes and should not be considered medical advice. It is important to note that the information presented here is not meant to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Prior to embarking on any new health-related regimen, Always consult your healthcare provider before trying new supplements or treatments. Keeping you safe and well is our top priority. Additionally, it’s important to note that the FDA has not endorsed any claims regarding the health benefits of cannabis. Delta8Hub makes no guarantees or warranties regarding the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any messages contained here in.