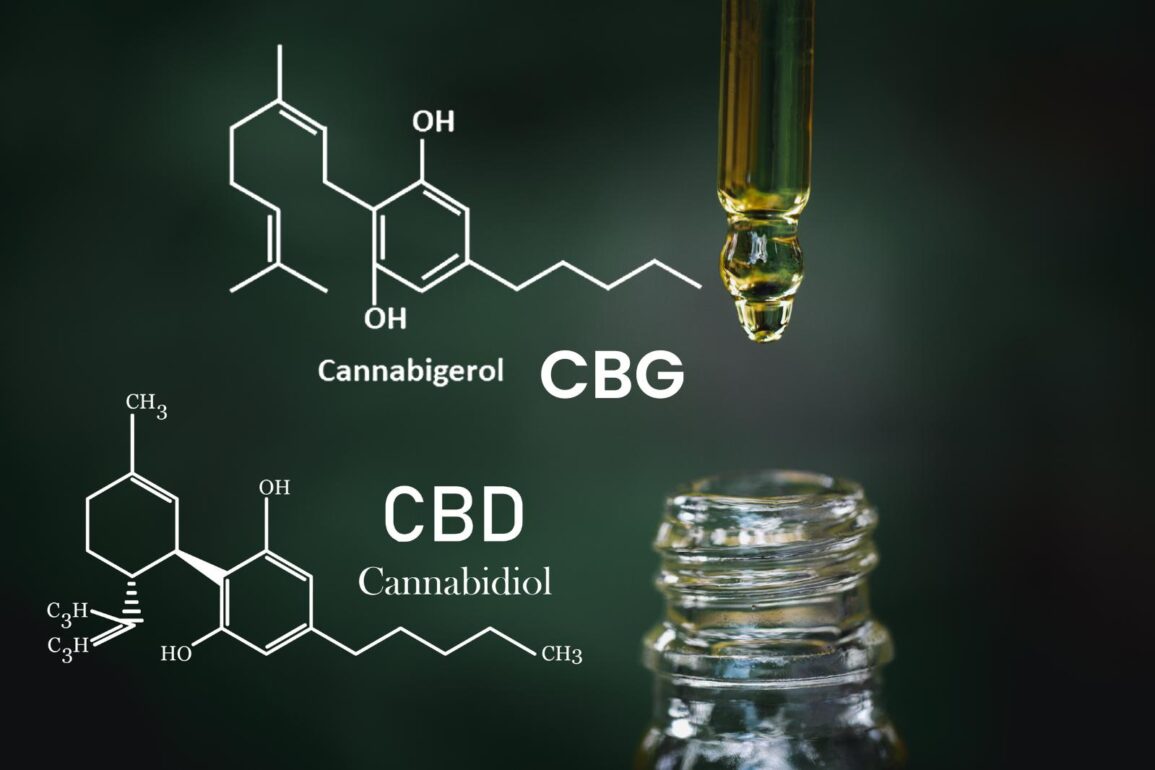
In recent years, the world of cannabinoids has expanded beyond just THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the psychoactive compound found in cannabis. CBD (cannabidiol) and CBG (cannabigerol) have gained significant attention for their potential health benefits, but what sets them apart? Let’s delve into the nuances of CBD and CBG to understand What Is CBG Vs. CBD.
Table of Contents
- What are They?
- What is the Difference Between CBD and CBG?
- Can CBD or CBG Cause a High?
- Are They Both Legal?
- Therapeutic benefits of CBD
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties
- Assisting Smoking Cessation and Dealing with Withdrawal
- Seizures
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Anxiety Disorders: A Global Struggle
- Therapeutic Benefits of CBG for Anxiety
- Is it Safe to Take CBD and CBG Simultaneously?
- Summary: Harnessing CBG’s Potential for Anxiety Relief
- FAQs
What are They?
CBD (Cannabidiol)
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a non-psychoactive compound extracted from cannabis and hemp plants. It is known for its potential therapeutic effects, ranging from anxiety and pain relief to anti-inflammatory properties. Unlike THC, CBD doesn’t induce a “high” or altered state of mind, making it an appealing option for those seeking relief without the euphoric effects of cannabis use.
CBG (Cannabigerol)
CBG, or cannabigerol, is another non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis and hemp plants. Often referred to as the “mother cannabinoid,” CBG is a precursor to other cannabinoids, including THC and CBD. It’s typically present in smaller quantities than CBD or THC, making it a rarer and more sought-after compound. CBG has garnered attention for its potential neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties.
What is the Difference Between CBD and CBG?
While CBD and CBG are non-psychoactive compounds with potential therapeutic benefits, they have distinct mechanisms of action and possible uses.
- Targeted Effects: CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) by indirectly influencing cannabinoid receptors. This interaction contributes to its anti-anxiety, pain-relieving, and anti-inflammatory effects. On the other hand, CBG is thought to interact directly with both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the ECS, potentially explaining its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Potential Medical Applications: CBD has gained widespread recognition for its potential in treating various conditions, such as epilepsy, anxiety, and chronic pain. CBG, though less studied, shows promise in treating glaucoma, inflammatory bowel disease, and neurodegenerative conditions.
- Synergy: Some researchers suggest that CBD and CBG may work synergistically when combined, enhancing each other’s therapeutic effects in what’s known as the entourage effect. This phenomenon highlights the potential benefits of using whole-plant extracts containing multiple cannabinoids and terpenes.
Can CBD or CBG Cause a High?
One of the primary distinctions between CBD, CBG, and THC is their psychoactivity. THC is the compound responsible for the intoxicating “high” associated with cannabis use. However, CBD and CBG are non-intoxicating, meaning they don’t produce the altered state of consciousness that THC does. This characteristic makes them attractive options for those seeking the potential health benefits of cannabinoids without the mind-altering effects.
Are They Both Legal?
The legality of CBD and CBG varies depending on the jurisdiction and the source of the compounds. In many parts of the world, CBD extracted from industrial hemp (containing less than 0.3% THC) is legal as long as it adheres to specific regulations. CBG’s legality follows a similar pattern, although it may be subject to more stringent regulations due to its relatively low presence in hemp plants.
It’s crucial to note that the legal landscape surrounding cannabis and its derivatives is evolving rapidly, so staying informed about the regulations in your region is recommended.
In conclusion, while CBD and CBG share similarities as non-psychoactive cannabinoids with potential therapeutic benefits, they also possess unique characteristics that set them apart.
Their different mechanisms of action, possible medical applications, and non-intoxicating nature make them intriguing subjects for ongoing research and exploration. As the scientific community continues to uncover the depths of these cannabinoids, individuals can make informed choices about incorporating them into their wellness routines. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new health regimen, especially when considering the use of cannabinoids like CBD or CBG.
Therapeutic benefits of CBD
CBD (cannabidiol), a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis and hemp plants, have garnered immense attention for its potential therapeutic uses. CBD’s versatility has led to its integration into various wellness regimens, from addressing physical discomfort to alleviating mental distress. Let’s delve into some of the notable therapeutic benefits of CBD:
- Pain Management and Inflammation Relief: CBD’s potential as a natural pain reliever is one of its most celebrated attributes. It interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which regulates pain perception and inflammation. Studies suggest CBD may help reduce chronic pain associated with arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and fibromyalgia. Its anti-inflammatory properties contribute to its effectiveness in this regard.
- Anxiety and Stress Reduction: CBD’s anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) properties have garnered attention for their potential to alleviate various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). By interacting with neurotransmitter systems related to mood regulation, CBD may help promote relaxation and a sense of calm without inducing the intoxicating CBG effects associated with THC.
- Sleep Improvement: Individuals struggling with insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns may find relief with CBD. Its calming effects and potential impact on sleep-wake cycles have made it a subject of interest for those seeking a natural way to improve sleep quality.
- Epilepsy and Seizure Management: One of CBD’s most well-established therapeutic uses is in treating epilepsy, particularly in rare and treatment-resistant forms. The FDA has approved Epidiolex, a CBD-based medication, for specific epilepsy conditions. CBD’s anticonvulsant properties are believed to contribute to its ability to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
- Neurological Disorders: CBD’s neuroprotective properties make it an appealing candidate for managing various neurological conditions, including Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis. While research is ongoing, preliminary studies suggest that CBD’s interaction with the ECS and its anti-inflammatory effects might positively impact neurodegenerative disorders.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
One of CBD’s most celebrated attributes is its potent anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to harmful stimuli. Still, when it becomes chronic, it can lead to various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune disorders, and chronic pain conditions like arthritis. CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and various receptors in the body, potentially modulating the inflammatory response and relieving individuals suffering from inflammatory conditions. As a result, CBD-based products are increasingly being explored as complementary therapies for managing pain and improving overall quality of life.
Assisting Smoking Cessation and Dealing with Withdrawal
Smoking cessation can be incredibly challenging, often accompanied by intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms. CBD has emerged as a potential ally in this battle against nicotine addiction. Research suggests that CBD may influence the brain’s reward system by interacting with receptors associated with addiction. Furthermore, it might alleviate anxiety and stress, common triggers for relapse during the cessation process. Several studies have explored the use of CBD in reducing cigarette consumption and nicotine dependence, offering hope for a novel approach to quitting smoking.
Seizures
One of CBD’s most well-known success stories in the medical world revolves around its role in managing seizures, particularly in rare forms of epilepsy like Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Epidiolex, a CBD-based medication, received FDA approval in 2018 to treat these severe forms of epilepsy. CBD’s anticonvulsant properties are believed to stem from its interaction with neurotransmitter systems and its potential to dampen excessive neuronal activity. The effectiveness of CBD in reducing the frequency and severity of seizures has provided a new ray of hope for patients who previously had limited treatment options.
Alzheimer’s Disease
The potential of CBD to mitigate the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, has also captured the attention of researchers. Alzheimer’s is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein deposits and inflammation in the brain, leading to cognitive decline and memory loss. CBD’s multifaceted properties, including its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective effects, make it an intriguing candidate for addressing various aspects of the disease. While research is still in its early stages, preliminary findings indicate that CBD might help reduce neuroinflammation and promote neurogenesis, potentially slowing down the progression of Alzheimer’s and improving patients’ quality of life.
Anxiety Disorders: A Global Struggle
Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and more. These disorders are characterized by excessive worry, fear, and heightened stress responses, often interfering with daily life. Conventional treatments, such as therapy and medication, have proven effective for many, but some individuals seek complementary approaches to manage their symptoms.
Therapeutic Benefits of CBG for Anxiety
Cannabigerol (CBG), often referred to as the “stem cell” of cannabinoids, is gaining prominence for its potential therapeutic benefits. While research on CBG is still in its early stages, some studies suggest that CBG may play a role in reducing anxiety and promoting relaxation.
CBG’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) is believed to contribute to its anxiolytic effects. The ECS regulates mood, stress responses, and emotional well-being. CBG’s interaction with ECS receptors, specifically CB1 and CB2, may help modulate these processes and alleviate anxiety-related symptoms.
Is it Safe to Take CBD and CBG Simultaneously?
CBD and CBG are non-psychoactive cannabinoids, meaning they don’t induce the “high” associated with THC. Combining them is generally considered safe, but it’s essential to approach their usage thoughtfully. As with any wellness approach, individual responses can vary, so consulting a healthcare professional before starting a CBD and CBG regimen is recommended, especially if you’re taking other medications.
Combining CBD and CBG can potentially enhance their effects through what’s known as the entourage effect. This concept suggests that different cannabinoids and terpenes, when used together, may have a synergistic effect, magnifying their therapeutic potential. However, more research is needed to understand this synergy’s extent fully.
Summary: Harnessing CBG’s Potential for Anxiety Relief
In summary, the quest for alternative anxiety treatments has paved the way for exploring cannabinoids like CBG. While CBG’s potential benefits for anxiety are promising, it’s essential to approach its use with a balanced perspective. As research continues, individuals interested in using CBG to manage stress should consider the following:
- Consult a Professional: Before introducing any new supplement into your routine, especially for anxiety management, consult a healthcare provider. They can offer personalized guidance based on your medical history and current condition.
- Quality Matters: Choose reputable brands with third-party lab testing to ensure product quality and potency.
- Start Slow: Begin with a lower dose and gradually increase it as needed. Everyone’s body responds differently, so finding the proper dosage for you might require some experimentation.
- Monitor Your Response: Pay attention to how your body responds to CBG. Note any changes in your anxiety symptoms, mood, or overall well-being.
- Consider Combination: If desired, explore the potential synergy by combining CBD and CBG. However, proceed with caution and, again, consult a healthcare professional.
FAQs
CBG vs. CBD
CBG (cannabigerol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are two distinct cannabinoids in cannabis and hemp plants, each with unique properties and potential therapeutic benefits. While they share some similarities, their differences set them apart. Let’s compare CBG and CBD:
1. Chemical Structure:
- CBG: Known as the “stem cell” or “parent” cannabinoid, CBG is a precursor to other cannabinoids, including CBD and THC. It is often present in deficient concentrations in mature cannabis plants and is converted into other cannabinoids as the plant grows.
- CBD: Cannabidiol is a prominent non-psychoactive cannabinoid in higher concentrations in cannabis and hemp plants. It’s obtained by extracting CBD-rich oils from the plant’s flowers, leaves, and stems.
2. Interaction with Receptors:
- CBG: CBG is thought to interact directly with CB1 and CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system (ECS), although the exact mechanisms are still being studied.
- CBD: CBD doesn’t directly bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors but influences them indirectly. It can modify how these receptors interact with other cannabinoids, potentially modulating the effects of the ECS.
3. Potential Therapeutic Benefits:
- CBG: Although research is in its early stages, CBG has shown promise in several areas. It’s being explored for its potential anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and antibacterial properties. CBG’s ability to stimulate appetite and inhibit the growth of certain cancer cells is also being studied.
- CBD: CBD has gained recognition for its potential therapeutic benefits. It’s known for its anti-anxiety, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anticonvulsant properties. CBD is often used to manage anxiety disorders, epilepsy, chronic pain, and more.
What is CBG?
CBG (cannabigerol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are two distinct cannabinoids found in cannabis and hemp plants, each with unique properties and potential therapeutic benefits. While they share some similarities, their differences set them apart. Let’s compare CBG and CBD:
1. Chemical Structure:
- CBG: Known as the “stem cell” or “parent” cannabinoid, CBG is a precursor to other cannabinoids, including CBD and THC. It is often present in very low concentrations in mature cannabis plants, as it is converted into other cannabinoids as the plant grows.
- CBD: Cannabidiol is a prominent non-psychoactive cannabinoid in higher concentrations in cannabis and hemp plants. It’s obtained by extracting CBD oils from the plant’s flowers, leaves, and stems.
2. Interaction with Receptors:
- CBG: CBG is thought to interact directly with CB1 and CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system (ECS), although the exact mechanisms are still being studied.
- CBD: CBD doesn’t directly bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors but influences them indirectly. It can modify how these receptors interact with other cannabinoids, potentially modulating the effects of the ECS.
3. Potential Therapeutic Benefits:
- CBG: Although research is in its early stages, CBG has shown promise in several areas. It’s being explored for its potential anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and antibacterial properties. CBG’s ability to stimulate appetite and inhibit the growth of specific cancer cells is also being studied.
- CBD: CBD has gained recognition for its potential therapeutic benefits. It’s known for its anti-anxiety, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anticonvulsant properties. CBD is often used to manage anxiety disorders, epilepsy, chronic pain, and more.
What are CBG benefits
CBG, known for its potential anti-inflammatory properties, holds promise as a natural option for managing chronic pain and conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Preliminary studies suggest that CBG’s neuroprotective effects could contribute to innovative therapies for neurodegenerative disorders, providing hope for improved quality of life.
What is CBG good for?
CBG (cannabigerol) is believed to have several potential benefits, though it’s important to note that research is still in its early stages. Some areas where CBG shows promise include
- Inflammation: CBG’s anti-inflammatory properties make it a candidate for managing conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Pain Relief: Due to its potential interactions with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), CBG may offer relief from chronic pain associated with various conditions.
- Neuroprotection: CBG’s neuroprotective effects could make it useful in developing therapies for neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
- Antibacterial Properties: Initial research suggests that CBG might be effective against certain antibiotic-resistant bacteria, highlighting its potential as an antibacterial agent.
- Appetite Stimulation: CBG may stimulate appetite, which could benefit individuals dealing with appetite loss due to medical treatments or conditions.
What does CBG do?
While research is ongoing and our understanding is still evolving, CBG is believed to have various potential effects due to its interaction with ECS receptors. Some of the actions CBG might have include:
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: CBG is thought to interact with both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the ECS, which could contribute to its potential anti-inflammatory properties. This makes CBG a candidate for managing conditions marked by chronic inflammation, such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Neuroprotective Properties: CBG’s interaction with ECS receptors might have neuroprotective effects. This could be particularly relevant for conditions like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, where neurodegeneration is a key factor.
- Antibacterial Activity: Some research suggests that CBG could possess antibacterial properties, potentially making it helpful in addressing antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- Appetite Stimulation: CBG may stimulate appetite, which could benefit individuals dealing with appetite loss due to medical treatments or conditions like cancer.
- Glaucoma Management: CBG has been investigated for its potential to reduce intraocular pressure, a factor in glaucoma. This could make it a candidate for glaucoma management.
In conclusion, CBG’s potential therapeutic benefits for anxiety offer a glimmer of hope for those seeking alternative solutions. As science unravels the intricacies of cannabinoids and their effects on mental health, the collaborative efforts of researchers, healthcare providers, and individuals can pave the way for more comprehensive and personalized approaches to anxiety management.
Disclaimer – The contents of this article are provided solely for informational purposes and should not be considered medical advice. It is important to note that the information presented here is not meant to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Prior to embarking on any new health-related regimen, Always consult your healthcare provider before trying new supplements or treatments. Keeping you safe and well is our top priority. Additionally, it’s important to note that the FDA has not endorsed any claims regarding the health benefits of cannabis. Delta8Hub makes no guarantees or warranties regarding the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any messages contained here in